
Especially a concern where surfaces are flat.Line of Sight propagation is subject to.Subject to signal reflections from the terrain.Important in the calculation of distance. Height of TX and RX antennas above terrain is.For terrestrial application distance is limited.Space wave, line of sight, and tropospheric.VHF signals and higher are not normally returned.To the transmitter that will not receive the Forįrequencies above fc there will be a region close ( 0.85 MUF)Īs the angle of elevation increases the distanceĬovered decreases and MUF becomes lower. The highestįrequency that returns to earth for a given path. Ionospheric sounding - determines Critical.Frequency Diversity - transmit on multiple.D and E layers absorb low frequencies( 8-10Mhz).Signal returns by a form of refraction.Ionization increases with altitude and is greater.Three main regions d, E, anf F layers(F1 and F2).Ground waves attenuate quickly above 2 Mhz.Further from transmitter the more horizontal the.Vertically polarized in order to minimizeĬurrents induced in the ground creating losses.Obstruction are small compared to wavelength. Diffraction more pronounced when dimensions of.Obstruction and radiate in the area beyond. Some wavefronts pass beside or above the.Assume that each point on a wavefront presents.Light appears to go around corners periodically.Total internal reflection occurs in optcalįibres. Reflection is optical fibre.( core and cladding)Ĭan be used to determine angles of incident and An application example of total internal.Travels to area of low dielectric constant.Įxtreme case is total internal reflection) When wave enters a region with a higherĭielectric constant ( a lower propagation.When there is a transition from one medium to.Diffuse reflection collective orientation is.With both angles measured from a line normal to

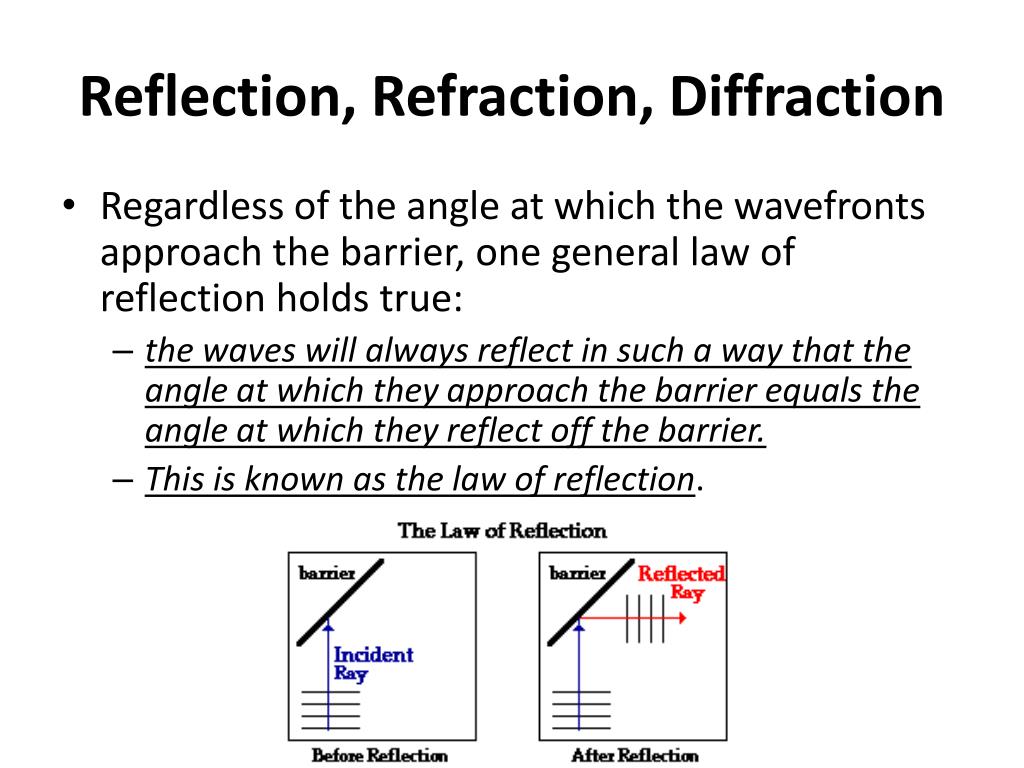
Angle of incidence equals angle of reflection.The following two videos cover the wide range of wave behaviour, including reflection, refraction, diffraction and wave superposition.Title: Reflection, Refraction, and Diffraction Wave superposition occurs when two or more waves are travelling through the same medium at the same time, the net displacement at any point in time, is simply the sum of the individual wave displacements. Diffraction is the bending of waves around obstacles and openings. Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated, while refraction is the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another. In this post, we explain the behaviour of waves in a variety of situations by investigating the phenomena of reflection, refraction, diffraction and wave superposition, as a part of the Prelim Physics course under the module Waves and Thermodynamics and sub-part Wave Behaviour. What is reflection, refraction, diffraction and wave superposition? Latent Heat Involved in a Change of State.Relationship between the Change in Temperature of an Object and its Specific Heat Capacity (Q = mc△T).Relationship Between the Temperature of an Object and Kinetic Energy.Applying Equations and Relationships to Solve Questions (Refraction Index, Snell's Law, Critical Angle, Intensity of Light).Relationship Between the Inverse Square Law, the Intensity of Light and the Transfer of Energy.Practical Investigation: Phenomenon of the Dispersion of Light.Refraction and Total Internal Reflection.Practical Investigation: Formation of Images in Mirrors and Lenses.Behaviour of Standing Waves on Strings and Pipes.Reflection, Diffraction, Resonance and Superposition of Sound Waves.Relationship Between Distance and Intensity of Sound.Displacement of Air Molecules as Variations in Pressure.Practical Investigation: Pitch and Loudness of a Sound.Resonance in Mechanical Systems (Driving Frequency, Natural Frequency, Amplitude, Transfer of Energy).Reflection, Refraction, Diffraction and Wave Superposition.Graphs of Displacement as a Function of Time (Transverse and Longitudinal Waves).Practical Investigation: Transverse, Longitudinal, Mechanical and Electromagnetic Waves.Practical Investigation: Creation of Mechanical Waves.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
